
Pediatric Urology
Pediatric Urology
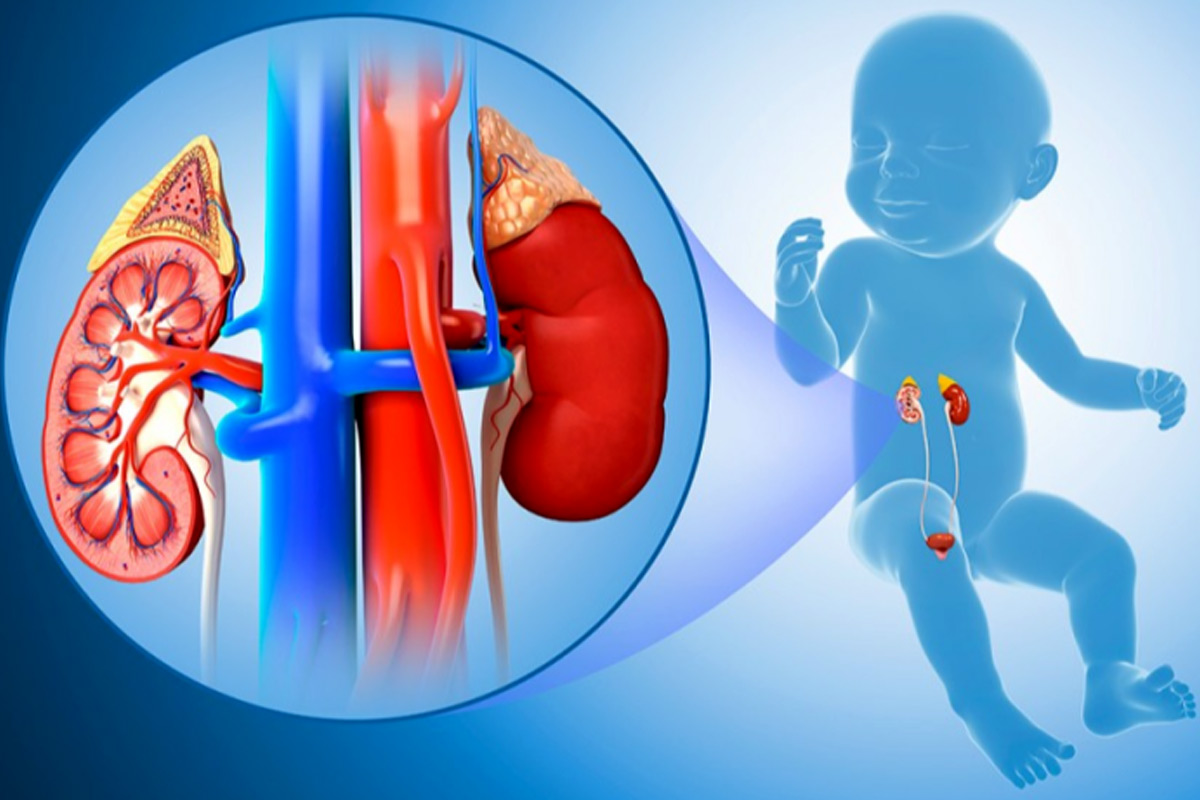
Pediatric urology is a subspecialty of urology focused on the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract and genital problems in children. This field deals with a wide range of congenital and acquired conditions affecting the kidneys, bladder, urethra, and genital organs in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatric urologists are medical doctors who have undergone additional training to specialize in the unique urological needs of young patients.
Here are some common conditions and areas of concern addressed by pediatric urologists:
-
Congenital Anomalies: Pediatric urologists often manage congenital conditions present at birth, such as hypospadias (an abnormal positioning of the urethral opening in males), cryptorchidism (undescended testicles), vesicoureteral reflux (a condition where urine flows backward from the bladder to the kidneys), and posterior urethral valves (a blockage in the urethra).
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Children are susceptible to UTIs, and recurrent or severe infections may require urological evaluation to determine underlying causes and prevent further episodes.
-
Voiding Dysfunction: Problems with urination, including urinary incontinence, urgency, and difficulty emptying the bladder, can affect children and may be addressed by pediatric urologists.
-
Kidney Stones: Though less common in children than in adults, kidney stones can develop and may require surgical intervention or other treatments.
-
Neurogenic Bladder: Some children with neurological conditions or spinal cord abnormalities may have impaired bladder function, which pediatric urologists can manage.
-
Tumors: Pediatric urologists may diagnose and treat tumors in the urinary tract, including Wilms' tumors (a type of kidney cancer) and testicular or ovarian tumors.
-
Reconstructive Surgery: Surgical procedures may be needed to correct structural abnormalities or to reconstruct damaged organs following trauma or illness.
-
Genital Surgery: Pediatric urologists perform surgeries related to genital anomalies in both males and females, including procedures like circumcision and genital reconstruction.
Pediatric urologists work closely with other medical specialists, including pediatricians, neonatologists, nephrologists, radiologists, and pediatric surgeons, to provide comprehensive care for their young patients. They also understand the unique emotional and psychological aspects of working with children and their families and strive to create a supportive and child-friendly environment.
Advancements in minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as laparoscopy and robotics, have allowed for less invasive treatments and faster recoveries for many pediatric urological conditions. Overall, pediatric urology plays a vital role in ensuring the health and well-being of children with urinary and genital issues, offering both medical and surgical solutions to improve their quality of life.